RFID Cabinet Device
SDK Development Instructions
Document Version | Date | Author | Description |
1.0.0 | 2025-06-04 | newintelliconnect | First Edition |
I. Overview
This document is intended to provide Android software developers (hereinafter referred to as "users") with functional descriptions, integration instructions, and precautions for the RFID cabinet device SDK, enabling users to develop third-party application Apps based on this document to manage RFID cabinets.
II. Hardware instructions
The RFID intelligent cabinet includes hardware devices such as a mainboard, a temperature and humidity monitoring device, a fingerprint device, an intelligent door lock device, an IC card reader, and an RFID antenna. These devices can be monitored and their data can be read through the SDK interface, so as to complete the control of the RFID intelligent cabinet.
The SDK mainly controls the hardware through the mainboard of the RFID intelligent cabinet (hereinafter referred to as the "device"). In all the interfaces of this document, "device" (or "tcpDevice") refers to the TcpDevice class corresponding to the RFID smart cabinet.
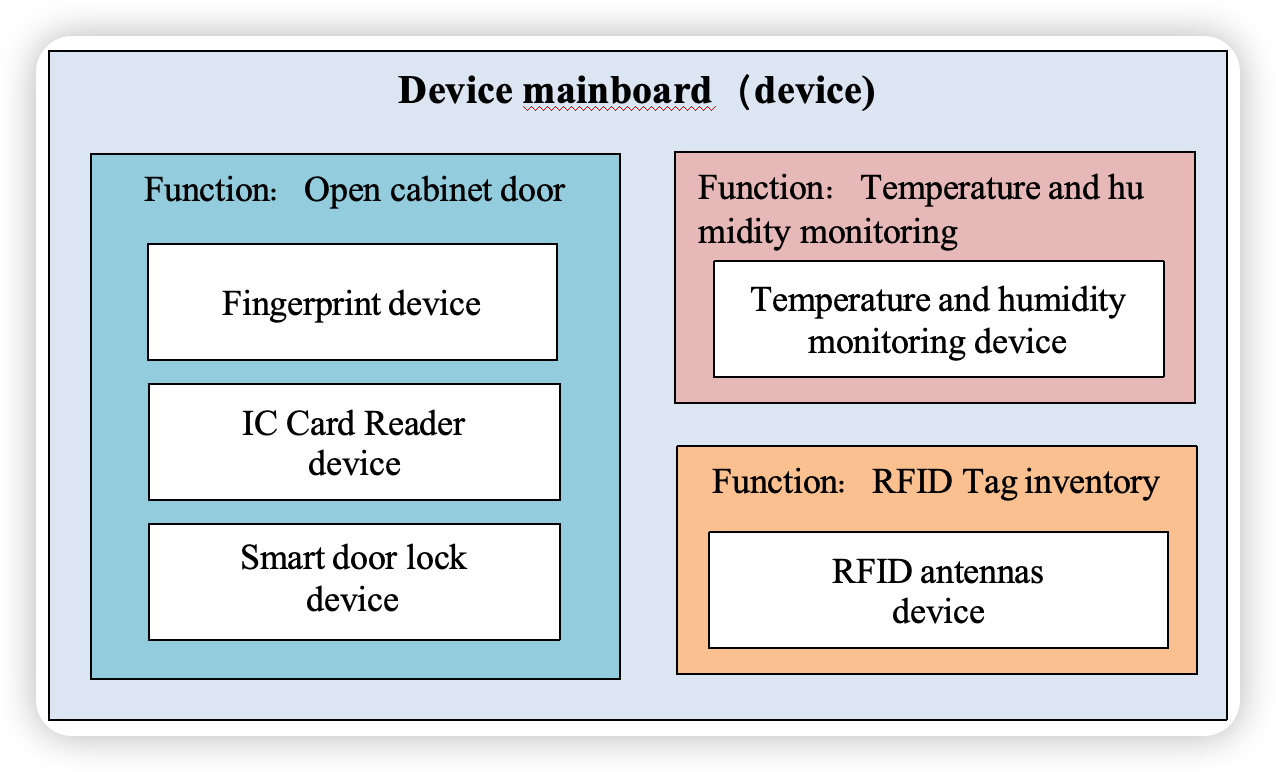
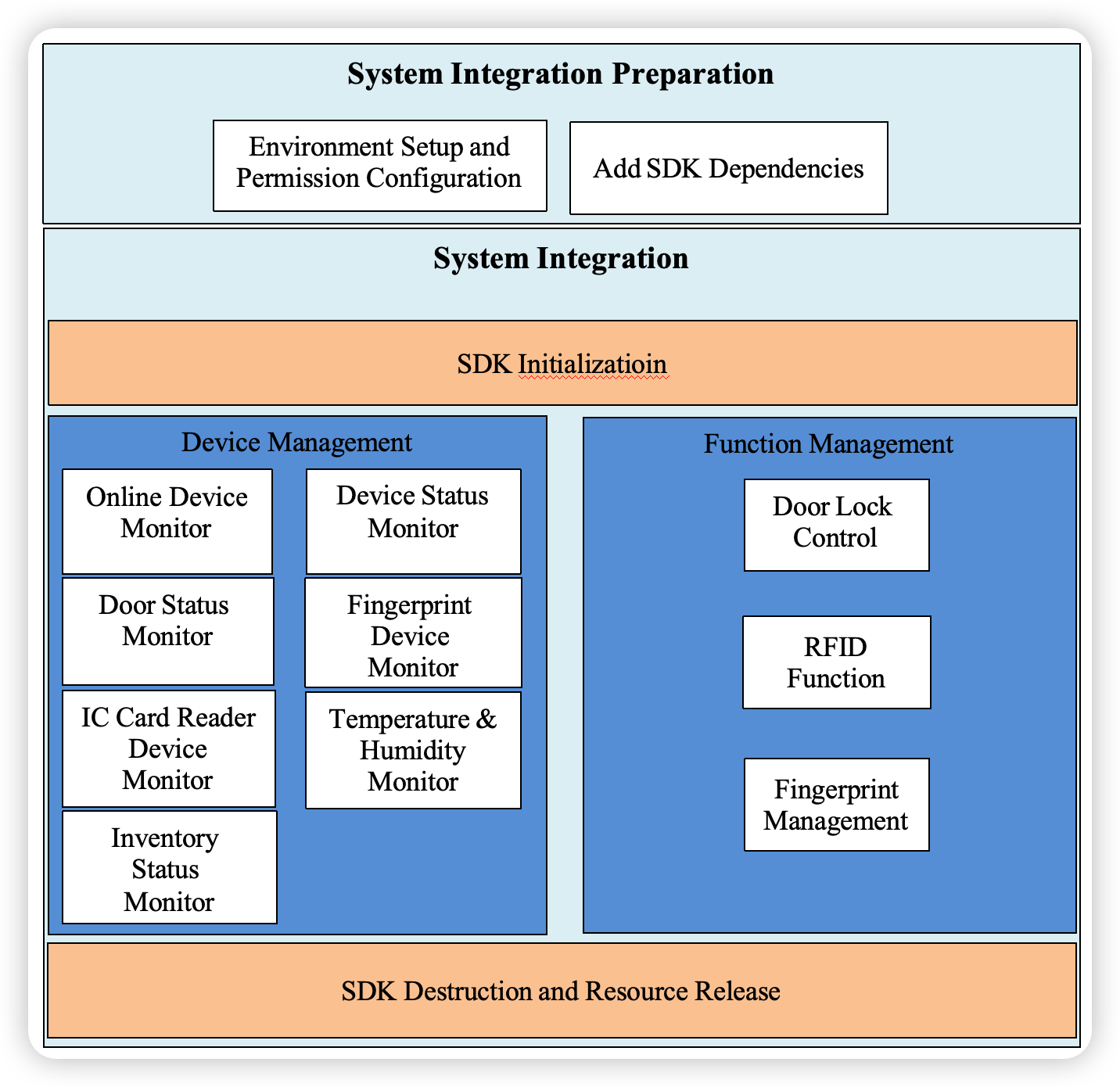
III. SDK Integration Instructions
• System integration preparation: including environment setup, permission configuration, and adding SDK dependency packages.
• System integration: involving SDK initialization, function management, device management, door lock control, various device status monitoring (such as online devices, device status, door status, fingerprint devices, RFID functions, temperature/humidity, card readers, inventory status, etc.), as well as SDK destruction and resource release.
IV. Environment Requirements and Permission Configuration
l SDK Usage Environment Requirements
1. Android system version: Android 5.0 (API 21) or higher
2. Development environment requirements:
◦ Recommended Android Studio 3.0 or higher
◦ Recommended Gradle 6.1.1 or higher
◦ Recommended JDK 1.8 or higher
1. Network requirements:
◦ Support TCP/IP network connections
◦ Devices and the host (Android device) must be on the same local area network
◦ Ensure the host (Android device) network port (default 5464) is not occupied
◦ Default IP of the host (Android device): 192.168.1.140
◦ Default IP of the device: 192.168.1.X (X is 50 or higher, e.g., 192.168.1.50, 192.168.1.51, etc.)
l APP Required Permissions
<!-- 网络权限 --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" /> <!-- 存储权限(保存日志用) --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> |
Add the following permissions in AndroidManifest.xml:
Note: For Android 6.0 and above, dynamic permission requests are required at runtime.
V. Adding File Dependencies
System provides two methods to add SDK development packages. Users can choose the appropriate method to download the corresponding files according to their own development environment.
Method 1: AAR File
System provides the AAR file, which users can directly add as a reference. Specific steps are as follows:
1. Place the TcpIotSdk_RFID-1.0.1.aar file in the libs folder of the application module.
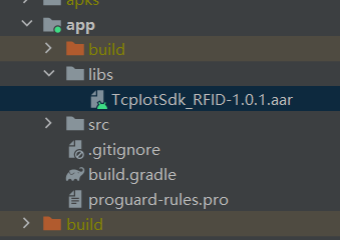
2. Add the dependency in the build.gradle of the application's app module:
dependencies { implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.aar']) // Or directly specify the AAR file // implementation files('libs/TcpIotSdk_RFID-1.0.1.aar') } |
Method 2: Remote Repository Dependency
System provides the SDK remote repository address, which users need to configure correctly in their projects. :
1. Add the Gradle repository URL to the .gradle file (e.g., build.gradle) in your project.
allprojects { repositories { ... maven { url 'https://wawasai-maven.pkg.coding.net/repository/tcpiotsdk/android/' } } } |
2. Add the dependency to the build.gradle file in the app module directory of the project.
dependencies { // Modify the version number according to actual needs implementation 'com.yufeikeji.android:TcpIotSdk_RFID:1.0.1' } |
VI. SDK Function Description
The main entry point of the SDK is the static TcpSdk class, as shown below.
TcpSdk.getInstance().init(context, new InitCallback() |
1. Function List
Function Category | Function Name | Description |
Basic Functions | SDK Initialization | Initialize the SDK and establish a connection with the device |
SDK Destruction | Release SDK resources and disconnect from the device | |
Device Management | Online Device Monitoring | Monitor device connection status |
Device Status Monitoring | Monitor door status, inventory status, temperature/humidity changes, etc. | |
Door Status Monitoring | Monitor door opening and closing events | |
IC Card Reader Monitoring | Monitor card swiping events of card readers | |
Fingerprint Device Monitoring | Monitor fingerprint device matching events | |
Temperature/Humidity Monitoring | Monitor temperature/humidity changes | |
Inventory Status Monitoring | Monitor changes in device inventory status | |
Fingerprint Management | Query Fingerprint Count | Get the number of registered fingerprints |
Register Fingerprint | Register a new fingerprint | |
Stop Registration | Stop the fingerprint registration process | |
Get Fingerprint Features | Get registered fingerprint features | |
Insert Fingerprint Features | Insert fingerprint feature data | |
Delete Fingerprint | Delete a specified fingerprint | |
Delete All Fingerprints | Delete all registered fingerprints | |
RFID Functions | Set Wireless Power | Set RFID read/write power |
Start Inventory | Start RFID tag inventory | |
Stop Inventory | Stop RFID tag inventory | |
Get Inventory Status | Get the current inventory status | |
Door Lock Control | Get Door Lock Status | Get the door lock's open/closed status |
Control Door Opening | Control the door lock's open/closed state |
2. Function Details
2.1. Basic Functions
2.1.1. Initialization
Initialize the SDK and establish a connection with the device. This is the first step in using the SDK and must be called before any other operations.
// Initialize SDK TcpSdk.getInstance().init(context, new InitCallback() { @Override public void onInitFinished(boolean success, String message) { if (success) { // The initialization is successful, the device monitoring can be started. . } else { // Initialization failed } |
Parameter Description:
• context: Application context, used for SDK initialization.
• InitCallback: Initialization callback interface
◦ onInitFinished: Initialization completion callback
▪ success: Whether initialization was successful
▪ message: Initialization result message
2.1.2. Destruction
Call this function when exiting the application or no longer using the SDK.
// Destroy SDK TcpSdk.getInstance().destroy(context, new DestroyCallback() { @Override public void onDestroyFinished(boolean success, String message) { if (success) { // Destruction successful } else { // Destruction failed } } |
Parameter Description:
• context: Application context
• DestroyCallback: Destruction operation callback interface
◦ onDestroyFinished: Destruction completion callback
▪ success: Whether destruction was successful
▪ message: Destruction result message
Note: When exiting the program, release monitoring resources first, and finally call destroy to release the SDK.
// Destroy online device monitor(refer to the subsequent “Device Management”) TcpSdk.getInstance().removeDeviceListener(mOnDeviceChangeListener) // Destroy device status monitor TcpSdk.getInstance().removeBoardListener(mSimpleBoardListener) ...... // Destroy SDK TcpSdk.getInstance().destroy(this) |
2.2. Device Management
Device management is mainly responsible for monitoring device events and status changes and providing real-time callbacks.
Monitoring resources need to be released when the system exits.
TcpSdk.getInstance().removeDeviceListener(mOnDeviceChangeListener) |
2.2.1. Online Device Monitoring
Monitor device online/offline status changes, and trigger real-time callbacks when devices go online or offline. Users can obtain currently online devices through this interface.
// Add device status change TcpSdk.getInstance().addDeviceListener(new OnDeviceChangeListener() { @Override public void onDeviceChanged(List<TcpDevice> devices) { // Callback is generated when the device goes online or offline. } }); |
Parameter Description:
• OnDeviceChangeListener: Interface for monitoring device changes
◦ onDeviceChanged: Callback when the device goes online or offline
▪ devices: List of currently online devices
Note: devices is a list of online devices, and any device going online or offline will trigger a callback through this monitoring. Only online devices are included in devices, with no offline devices. If a device goes offline (i.e., not in devices), related functions for that device cannot be called.
Data Object Description:
• TcpDevice: Data object representing a device
◦ getIp(): Get the device's IP address
when the system exits, the removeDeviceListener function needs to be called for release.
TcpSdk.getInstance().removeDeviceListener(deviceChangeListener) |
Note: In system function interfaces requiring device parameters, both of the following parameter passing methods are supported:
1. Directly pass the device object
2. Directly pass the device's IP address
Users can freely choose one of these methods according to their programming habits.
2.2.2. Device Status Monitoring
Device heartbeat monitoring, with a default callback generated once per second.
Note: The difference between "Device Status Monitoring" and "Online Device Monitoring":
• Device Status Monitoring: Monitor device heartbeat and returns device door status, inventory status, temperature/humidity, etc.
• Online Device Monitoring: Only monitor device online/offline status and does not trigger callbacks for other events.
// Method 1: Add via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().addBoardListener(deviceIp, new BoardListener() { @Override public void onReceiveState(TcpDevice tcpDevice, BoardState state) { // get door status boolean isDoorOpened = state.isDoorOpened(); // Get inventory status boolean isInventory = state.isInventory(); // Get temperature float temperature = state.getTemperature(); // Get humidity float humidity = state.getHumidity(); } }); // Method 2:Add via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().addBoardListener(device, new BoardListener() { @Override public void onReceiveState(TcpDevice tcpDevice, BoardState state) { } }); |
Parameter Description:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• BoardListener: Interface for monitoring device status
◦ onReceiveState: Callback triggered when status updates
▪ tcpDevice: Device object
▪ state: Device status object
Data Object Description:
• BoardState: Device status object
◦ isDoorOpened(): Get the current door status (true = open, false = closed)
◦ isInventory(): Get the current inventory status (true = inventory in progress, false = no inventory)
◦ getTemperature(): Get temperature value (unit: °C)
◦ getHumidity(): Get humidity value (unit: %)
when the system exits, the removeBoradListener function needs to be called for release.
TcpSdk.getInstance().removeBoardListener(boardChangeListener) |
2.2.3. Door Status Monitoring
Specifically monitor door status changes and triggers callbacks when door status changes. Compared to device status monitoring, this listener focuses more on door status changes.
// Method 1: Add via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().addDoorListener(deviceIp, new DoorListener() { @Override public void onDoorStateChanged(TcpDevice tcpDevice, int doorIndex, boolean isOpened) { // Callback when door status changes } }); // Method 2:Add via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().addDoorListener(device, new DoorListener() { @Override public void onDoorStateChanged(TcpDevice tcpDevice, int doorIndex, boolean isOpened) { // Callback when door status changes } }); |
Parameter Description:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• DoorListener: Door status monitoring interface
◦ onDoorStateChanged: Callback triggered when door status changes
▪ tcpDevice: Device object
▪ isOpened: Door status (true = open, false = closed)
when the system exits, the removeDoorListener function needs to be called for release.
TcpSdk.getInstance().removeDoorListener(doorChangeListener) |
2.2.4. Card Reader Monitoring (IC Card)
Monitor card swiping events of card reader and trigger callback when user swipe card.
// Method 1: Add via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().addCardListener(deviceIp, new CardListener() { @Override public void onReadCard(TcpDevice tcpDevice, String cardId) { // Callback when a card number is read } }); // Method 2:Add via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().addCardListener(device, new CardListener() { @Override public void onReadCard(TcpDevice tcpDevice, String cardId) { // Callback when a card number is read } }); |
Parameter Description:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• CardListener: Card reading monitoring interface
◦ onReadCard: Card reading callback
▪ tcpDevice: Device object
▪ cardId: card number
when the system exits, the removeCardListener function needs to be called for release.
TcpSdk.getInstance().removeCardListener(cardChangeListener) |
2.2.5. Fingerprint Device Monitoring
Monitor fingerprint device matching results and trigger callback when user log in with fingerprint.
// Method 1: Add via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().addFingerprintListener(deviceIp, new FingerprintListener() { @Override public void onResult(TcpDevice tcpDevice, TcpResponseMatch result) { // Fingerprint matching result callback } }); // Method 2:Add via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().addFingerprintListener(device, new FingerprintListener() { @Override public void onResult(TcpDevice tcpDevice, TcpResponseMatch result) { // Fingerprint matching result callback } }); |
Parameter Description:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• FingerprintListener: Fingerprint matching monitoring interface
◦ onResult: Matching result callback
▪ tcpDevice: Device object
▪ result: Matching result
Data Object Description:
• TcpResponseMatch: Data object representing fingerprint matching results
◦ isSuccess(): Whether matching was successful
◦ getUserId(): Get the matched user ID
◦ getFingerIndex(): Get the matched fingerprint index
when the system exits, the removeFingerprintListener function needs to be called for release.
TcpSdk.getInstance().removeFingerprintListener(fingerprintChangeListener) |
2.2.6. Temperature/Humidity Monitoring
Monitor temperature and humidity changes, triggering callback when values fluctuate.
// Method 1: Add via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().addTemperatureListener(deviceIp, new TemperatureListener() { @Override public void onTemperatureOrHumidityChanged(TcpDevice tcpDevice, double temperature,double humidity) { }); // Method 2: Add via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().addTemperatureListener(device, new TemperatureListener() { @Override public void onTemperatureOrHumidityChanged(TcpDevice tcpDevice, double temperature,double humidity) { } }); |
Parameter Description:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• TemperatureListener: Callback interface for temperature/humidity change
◦ onTemperatureOrHumidityChanged: Triggered when temperature or humidity change
▪ tcpDevice: Device object
▪ temperature: Temperature value (°C)
▪ humidity: Humidity value (%)
when the system exits, the removeTemperatureListener function needs to be called for release.
TcpSdk.getInstance().removeTemperatureListener(temperatureChangeListener) |
2.2.7. Inventory Status Monitoring
Monitor the start and end of device inventory, triggering callback when the inventory state change.
// Method 1: Add via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().addInventoryListener(deviceIp, new InventoryListener() { @Override public void onInventoryStateChanged(TcpDevice tcpDevice, boolean inventory) { } }); // Method 2: Add via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().addInventoryListener(device, new InventoryListener() { @Override public void onInventoryStateChanged(TcpDevice tcpDevice, boolean inventory) { } }); |
Parameter Description:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• InventoryListener: Callback interface for inventory status changes
◦ onInventoryStateChanged: Triggered when inventory starts or stops
▪ tcpDevice: Device object
▪ isInventory: true = inventory in progress, false = inventory stopped
when the system exits, the removeInventoryListener function needs to be called for release.
TcpSdk.getInstance().removeInventoryListener(inventoryChangeListener) |
2.3. Fingerprint Management
2.3.1. Enroll Fingerprint
// Method 1: Enroll via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().enroll(deviceIp, userId, fingerIndex, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseEnroll>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseEnroll data) { // enroll result if (data.getState() == TcpResponseEnroll.State.SUCCESS) { // Successful enrollment, get fingerprint feature String featureBase64 = data.getFeatureBase64(); } else if (data.getState() == TcpResponseEnroll.State.SCAN) { // Fingerprint scanned successfully, wait for next scan } else if (data.getState() == TcpResponseEnroll.State.ENROLLING) { // Enrollment in progress } else { // Enrollment failed (check error state) switch (data.getState()) { case NOT_MATCH: // Inconsistent fingerprints case TIMEOUT: // timeout case OVERFLOW: // Template capacity exceeded case ID_USED: // Index already in use case TOO_MANY_FINGERPRINT: // User has 10 registered fingerprints case WRONG_ID: // Invalid fingerprint index case DUPLICATE_FINGERPRINT: // Fingerprint already exists case FAIL: // General failure break; } } } }); // Method 2: Enroll via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().enroll(device, userId, fingerIndex, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseEnroll>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseEnroll data) { // Handle enrollment result } }); |
Parameters:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• userId: User ID (1-200)
• fingerIndex: Fingerprint index (1-10)
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseEnroll>: Callback for enrollment results
◦ onResult: Returns success status, message, and enrollment data
Data Object:
• TcpResponseEnroll: Enrollment result
◦ getState(): Enrollment status (SUCCESS, SCAN, ENROLLING, etc.)
◦ getFeatureBase64(): Base64-encoded fingerprint feature
◦ getStep(): Current scan step (1-3)
2.3.2. Stop Enrollment
Abort the fingerprint enrollment process.
// Method 1: Stop via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().stopEnroll(deviceIp, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseCancelEnroll>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseCancelEnroll data) { if (success) { // Enrollment stopped successfully } else { // Stop failed } } }); // Method 2: Stop via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().stopEnroll(device, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseCancelEnroll>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseCancelEnroll data) { // Handle stop result } }); |
Parameters:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseCancelEnroll>: Callback for stop result
◦ onResult: Returns success status and message
Data Object:
• TcpResponseCancelEnroll: Stop result
◦ getState(): Stop status
l SUCCESS
l FAIL
2.3.3. Delete Fingerprint
This function allows you to delete the fingerprint data under the specified device, user, and fingerprint index.
// Method 1: Delete single fingerprint via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().deleteFingerprint(deviceIp, userId, fingerIndex, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseDeleteFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseDeleteFeature data) { if (success) { // deleted successfully } else { // deleted failed } } }); // Method 2: Delete single fingerprint via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().deleteFingerprint(device, userId, fingerIndex, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseDeleteFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseDeleteFeature data) { } }); // Method 3: Delete all fingerprints for a user via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().deleteAllFingerprint(deviceIp, userId, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseDeleteFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseDeleteFeature data) { if (success) { // deleted successfully } else { // deleted failed } } }); // Method 4: Delete all fingerprints for a user via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().deleteAllFingerprint(device, userId, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseDeleteFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseDeleteFeature data) { } }); |
Parameters:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• userId: User ID (1-200)
• fingerIndex: Fingerprint index (1-10, omit for deleting all)
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseDeleteFeature>: Callback for deletion results
Data Object:
• TcpResponseDeleteFeature: Deletion result
◦ getState(): Deletion status
l SUCCESS: deleted successfully
l FAIL: deleted failed
l NOT_FOUND:fingerprint not exist
2.3.4. Delete All Fingerprint
This function deletes all fingerprint data on the specified device.
// Method 1: Delete all fingerprint via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().deleteAllFingerprint(deviceIp, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseDeleteFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseDeleteFeature data) { if (success) { // deleted successfully } else { // deleted failed } } }); // Method 2: Delete all fingerprint via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().deleteAllFingerprint(device, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseDeleteFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseDeleteFeature data) { } }); |
Parameters:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseDeleteFeature>: Callback for deletion results
Data Object:
◦ OnResult: result callbackl
▪ SUCCESS:Whether the operation is successfu
▪ message: operatuion result message
▪ data:Delete all fingerprint result data objects
Data Object:
• TcpResponseDeleteFeature: Deletion result object
◦ getState(): get deletion status
l SUCCESS: deleted successfully
l FAIL: deleted failed
2.3.5. Query Fingerprint Count
Retrieve the total number of registered fingerprints on a device.
// Method 1: Query via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().getFingerprintNumber(deviceIp, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetTotalNumber>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseGetTotalNumber data) { } }); // Method 2: Query via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().getFingerprintNumber(device, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetTotalNumber>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseGetTotalNumber data) { } }); // Method 3: Query the number of fingerprints for all devices. TcpSdk.getInstance().getFingerprintNumber(new TcpResponsesCallback<TcpResponseGetTotalNumber>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponses<TcpResponseGetTotalNumber> data) { } }); |
Parameters:
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: TcpDevice object
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetTotalNumber>: Callback for query results
◦ onResult: Returns success status, message, and data
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpResponseGetTotalNumber object
Data Object:
• TcpResponseGetTotalNumber:
◦ getTotalNumber(): Returns the total number of registered fingerprints
2.3.6. Get Fingerprint Features
Retrieve the feature data of a registered fingerprint.
// Method 1: Get fingerprint features via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().getFingerprintFeature(deviceIp, userId, fingerIndex, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseGetFeature data) { if (success) { // Get Base64-encoded feature data String featureBase64 = data.getFeatureBase64(); } else { } } }); // Method 2: Get fingerprint features via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().getFingerprintFeature(device, userId, fingerIndex, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseGetFeature data) { } }); |
Parameters:
• userId: User ID (1-200)
• fingerIndex: Fingerprint index (1-10)
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetFeature>: Callback for feature retrieval results
◦ onResult: Returns success status, message, and data
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpResponseGetFeature object
Data Object:
• TcpResponseGetFeature:
◦ getFeatureBase64(): Returns fingerprint feature in Base64
◦ getState(): Operation status
l SUCCESS
l FAIL
l NOT_FOUND
2.3.7. Insert Fingerprint Features
Manually insert pre-registered fingerprint feature data.
// Method 1: Insert fingerprint feature via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().insertFingerprintFeature(deviceIp, userId, fingerIndex, featureBase64, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseSetFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseSetFeature data) { if (success) { } else { } } }); // Method 2: Insert fingerprint feature via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().insertFingerprintFeature(device, userId, fingerIndex, featureBase64, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseSetFeature>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseSetFeature data) { } }); |
Parameters:
• deviceIp:设备IP地址
• device: 设备对象
• userId: 用户 ID(1-200)
• fingerIndex: 指纹索引(1-10)
• featureBase64: Base64-encoded fingerprint feature data
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseSetFeature>: Callback for insertion results
◦ onResult: Returns success status, message, and data
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpResponseGetFeature object
Data Object:
• TcpResponseSetFeature: Insert result data object
◦ getState():Operation status
l SUCCESS
l FAIL
l OVERFLOW: The template capacity has reached the maximum limit
l ID_USED:The use of this index
l TOO_MANY_FINGERPRINT: The current user has already registered ten fingerprints.
l WRONG ID: invalid fingerprint index
l DUPLICATE_FINGERPRINT:fingerprint already exists
2.4. RFID Functions
2.4.1. Set RFID Power
// Method 1: Set RFID power via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().setRfidPower(deviceIp, power, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseSetRfidPower>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseSetRfidPower data) { // Result of setting RFID power if (success) { // Success } else { // Failure } } }); // Method 2: Set RFID power via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().setRfidPower(device, power, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseSetRfidPower>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseSetRfidPower data) { // Result of setting RFID power } }); |
Parameter Description
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• power: RFID power enumeration value (21-33)
l LEVEL_21: power value 21
l LEVEL_22: power value 22
l LEVEL_23: power value 23
l LEVEL_24: power value 24
l LEVEL_25: power value 25
l LEVEL_26: power value 26
l LEVEL_27: power value 27
l LEVEL_28: power value 28
l LEVEL_29: power value 29
l LEVEL_30: power value 30(default)
l LEVEL_31: power value 31
l LEVEL_32: power value 32
l LEVEL_33: power value 33
◦ TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseSetRfidPower>: Callback interface for power setting results
◦ onResult: Returns success status, message, and data
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpResponseSetRfidPower object
Data Object Description
• TcpResponseSetRfidPower: Result data object for power setting
◦ getState(): Setting status
l SUCCESS
l FAIL
l INVALID_POWER
Notes
1. The power value ranges from 21 to 33, and the default value is 30.
2. The larger the power value is, the farther the reading distance will be, but the power consumption will also be higher.
3. It is recommended to select an appropriate power value according to the actual usage scenario.
4. After modifying the power value, you need to restart the inventory for the changes to take effect.
5. Setting the power value too high may affect the stability of the device.
6. Setting the power value too low may affect the reading effect.
2.4.2. Start Inventory
The inventory start function allows for the inventory of RFID tags within a specified time period, and it will automatically stop when the time is up.
// Method 1: Start timed inventory via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().startFixTimeInventory(deviceIp, mills, allowInterrupt, new TcpCallback<TcpInventoryResult>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpInventoryResult data) { // Result of timed inventory } }); // Method 2: Start timed inventory via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().startFixTimeInventory(device, mills, allowInterrupt, new TcpCallback<TcpInventoryResult>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpInventoryResult data) { // Result of timed inventory } }); // Method 3: Start timed inventory for all devices TcpSdk.getInstance().startFixTimeInventory(mills, allowInterrupt, new TcpResponsesCallback<TcpInventoryResult>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponses<TcpInventoryResult> data) { // Results for all devices } }); |
Parameter Description
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• mills: Inventory duration (milliseconds)
• allowInterrupt: Whether to allow interruptions (default: true)
l true: It is allowed for other operations (such as opening the door) to interrupt the inventory
l false: Other operations are not allowed to interrupt the inventory.
• TcpCallback<TcpInventoryResult>: Callback interface for inventory results
◦ onResult: result callback
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpInventoryResult object
Data Object Description
• TcpInventoryResult: Inventory result data object
◦ getEpcList(): List of scanned EPC tags
◦ isInterrupted(): Whether interrupted
• TcpResponses<TcpInventoryResult>: Results for all devices
◦ getResponses():Obtain the response data list of all devices.
◦ isSuccess(): all the operations successful
2.4.3. Stop Inventory
// Method 1: Stop inventory via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().stopInventory(deviceIp, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseStopInventory>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseStopInventory data) { // Result of stopping inventory if (success) { // Success } else { // Failure } } }); // Method 2: Stop inventory via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().stopInventory(device, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseStopInventory>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseStopInventory data) { // Result of stopping inventory } }); |
Parameter Description
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseStopInventory>: Callback interface for stop inventory results
◦ onResult: result callback
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpResponseStopInventoryobject
Data Object Description
• TcpResponseStopInventory: Stop inventory result data object
◦ getState(): Stop status
l SUCCESS
l FAIL
l NOT_INVENTORY:
2.4.4. Get Inventory Status
// Method 1: Get inventory status via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().getInventoryStatus(deviceIp, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetInventoryStatus>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseGetInventoryStatus data) { // Result of getting inventory status if (success) { boolean isInventory = data.isInventory(); int inventoryMode = data.getInventoryMode(); } else { // Failure } } }); // Method 2: Get inventory status via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().getInventoryStatus(device, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetInventoryStatus>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseGetInventoryStatus data) { // Result of getting inventory status } }); |
Parameter Description
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetInventoryStatus>: Callback interface for inventory status query
◦ onResult: result callback
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpResponseGetInventoryStatus object
Data Object Description
• TcpResponseGetInventoryStatus: Inventory status data object
◦ isInventory(): Whether inventory is ongoing
◦ getInventoryMode(): Inventory mode
l 0: normal
l 1: timed
◦ getState(): Query status
l SUCCESS
l FAIL
2.5 Door Lock Control
2.5.1 Control Door Opening
// Method 1: Open door via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().openDoor(deviceIp, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseOpenDoor>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseOpenDoor data) { // Result of door opening control if (success) { // Success } else { // Failure } } }); // Method 2: Open door via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().openDoor(device, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseOpenDoor>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseOpenDoor data) { // Result of door opening control } }); |
Parameter Description
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseOpenDoor>: Callback interface for door control results
◦ onResult: result callback
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpResponseOpenDoor object
Data Object Description
• TcpResponseOpenDoor: Door control result data object
◦ isSuccess(): Whether control succeeded
◦ getState(): Control status
l SUCCESS
l FAIL
l DOOR_ALREADY_OPENED
l DOOR_ERROR
2.5.2 Get Door Lock Status
// Method 1: Get door status via device IP address TcpSdk.getInstance().getDoorStatus(deviceIp, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetDoorStatus>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseGetDoorStatus data) { // Result of getting door status if (success) { boolean isDoorOpened = data.isDoorOpened(); } else { // Failure } } }); // Method 2: Get door status via device object TcpSdk.getInstance().getDoorStatus(device, new TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetDoorStatus>() { @Override public void onResult(boolean success, String message, TcpResponseGetDoorStatus data) { // Result of getting door status } }); |
Parameter Description
• deviceIp: Device IP address
• device: Device object
• TcpResponseCallback<TcpResponseGetDoorStatus>: Callback interface for door status query
◦ onResult: result callback
▪ success: Operation result
▪ message: Result description
▪ data: TcpResponseGetDoorStatus object
Data Object Description
• TcpResponseGetDoorStatus: Door status data object
◦ isDoorOpened(): Door status
l true: opened
l false: closed
◦ getState(): Query status
l SUCCESS
l FAIL
VII. Exception Descriptions
1. Initialization Exceptions
• Network Connection Error: When initializing the SDK, if the device fails to connect to the specified server or device, the initialization will fail. In this case, the onInitFinished method of InitCallback will return a success value of false, and specific error information, such as "Network connection failed", will be provided in the message field. Developers can check the network settings to ensure that the device can access the server normally.
• Insufficient Permissions: If the application fails to obtain the necessary permissions, such as network access permissions, file read and write permissions, etc., the initialization may fail. Developers need to declare the necessary permissions in the AndroidManifest.xml file of the application and request these permissions from the user at runtime.
2. Device Management Exceptions
• Device Not Connected: Operations fail if the device is offline; check connection status before use.
3. Fingerprint Management Exceptions
• Fingerprint Module Failure: When performing operations such as fingerprint registration and querying the number of fingerprints, if the fingerprint module malfunctions, it may lead to the failure of these operations. The onResult method of the TcpResponseCallback will return a success value of false, and specific error information, such as "Fingerprint module malfunction", will be provided in the message. Developers should regularly check the connection status of the fingerprint module to ensure that it is in a normal operating state.
• Invalid User ID/Fingerprint Index: When performing operations such as fingerprint registration or deletion, if the user ID or fingerprint index exceeds the allowed range (user IDs must be between 1-200 and fingerprint indices between 1-10), the operation may fail. Developers must verify that all parameters fall within the valid range before calling relevant APIs
4. RFID Function Exceptions
• RFID Antenna Failure: During operations such as setting wireless power or starting inventory checks, a malfunctioning RFID antenna may cause the operation to fail. The onResult method of TcpResponseCallback will return success as false, and the message field will contain specific error information, such as "RFID antenna malfunction." Developers should check the RFID antenna connection status to ensure it is functioning properly.
• Inventory Timeout: If the scheduled inventory check fails to complete within the specified time, the operation may fail. Developers should adjust the inventory time to ensure the operation completes successfully.
5. Door Lock Control Exceptions
• Door Lock Hardware Failure: When performing operations such as retrieving door lock status or controlling door opening, a malfunction in the door lock hardware may cause the operation to fail. The onResult method of TcpResponseCallback will return success as false, and the message field will provide specific error information, such as "Door lock hardware malfunction." Developers should check the door lock's connection status to ensure it is functioning properly.
VIII. Notes
1. After successful initialization, the SDK will automatically connect to the devices that were added last time.
2. When the application stops running, the destroy method needs to be called to release resources.
3. Adding a device will trigger an automatic connection, and deleting a device will automatically release resources.
4. If the IP port of the device changes, the previously added device needs to be deleted first, and then added again.
5. Operations related to fingerprint management:
◦ The user ID range is from 1 to 200.
◦ Each user supports a maximum of 10 fingerprints.
◦ When registering a fingerprint, you need to wait for the device prompt and continuously pay attention to the feedback messages.
◦ Registering a fingerprint requires pressing the finger three times, and each press needs to be completed within 7 seconds.
◦ During the fingerprint registration process, the stop registration method can be called at any time.
◦ After stopping the registration, the previously scanned fingerprint data will be cleared.
◦ Before obtaining the fingerprint features, ensure that a fingerprint has been registered under the corresponding user ID and fingerprint index.
◦ When deleting a specified fingerprint, ensure that a fingerprint has been registered under the corresponding user ID and fingerprint index.
◦ The operation of deleting a fingerprint cannot be restored, so please operate with caution.
6. Operations related to RFID:
◦ The wireless power value range is from 21 to 33.
◦ The larger the power value, the farther the reading distance, but the higher the power consumption.
◦ It is recommended to select an appropriate power value according to the actual usage scenario.
◦ After modifying the power value, the inventory needs to be restarted for the changes to take effect.
◦ The scheduled inventory will automatically stop after the specified duration, and there is no need to manually call the stop method.
◦ It is recommended to stop the inventory in a timely manner when it is not needed to save device resources.
◦ After stopping the inventory, the device will no longer return tag data.
◦ After the inventory is completed, all tag data of this inventory will be returned.
7. Operations related to door lock control:
◦ The door lock will automatically respond when its status changes.
◦ It is recommended to regularly check the status of the door lock.
◦ If there is an exception, promptly troubleshoot the hardware issues.
